What are Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers?
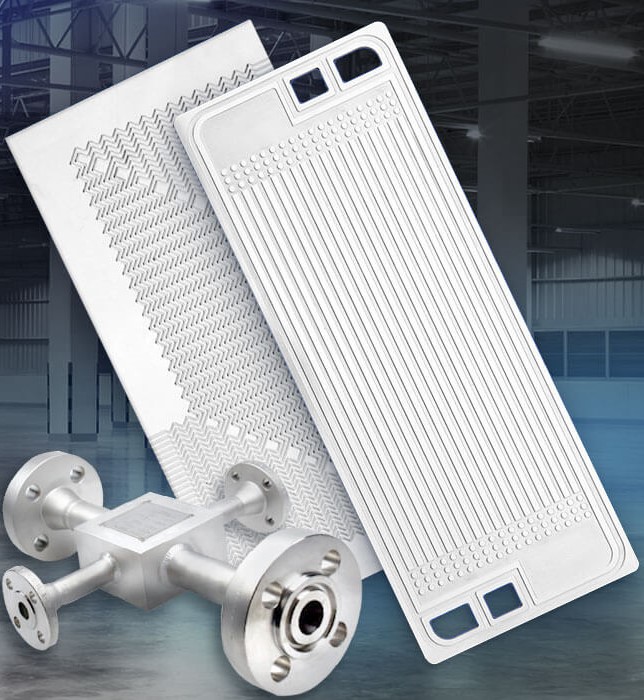
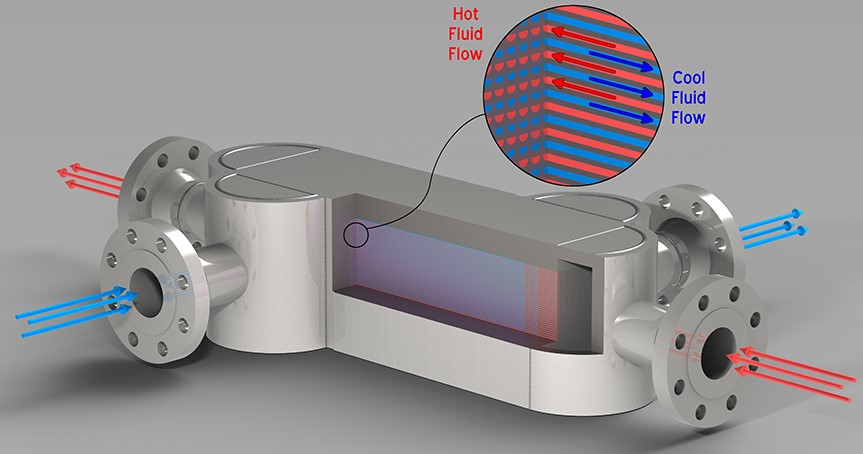
What exactly is printed circuit heat exchanger technology? A Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers (in short, PCHE) are also known as Diffusion-bonded Microchannel Heat Exchangers because of the microscopic fluid channels etched on the thin metal sheets from which they are manufactured. The printed circuit or tiny vessels for the fluid are chemically carved on these thin metal sheets. Different patterns for the separate hot fluid and cold fluid are carved on these sheets. Each type of fluid (hot or cold) has individual metal sheets with a carved pattern. There are multiple sheets like these for both fluids.
You alternately stack the metal sheets onto each other. The stacked sheets are diffusion bonded to form a mental block; it becomes a single, compact metal core instead of multiple metal sheets. This compact metal core has fluid vessels running through it. This is the printed circuit heat exchanger technology. Numerous such metal cores can be joined together by welding to form a more oversized printed circuit heat exchanger.
Printed Circuit Heat Exchanger is more beneficial than shell and tube heat exchange
Printed circuit heat exchangers can be big or small. However, compared to the shell and tube heat exchangers, these are pretty compact and can be up to 80% smaller than them. It is possible to manufacture PCHE that can withstand extremely high and low pressures and temperatures. Many problems arise in the shell and tube exchangers that do not rise in the printed circuit heat exchangers.
Moreover, they have many more advantages; it is highly flexible, multiple fluids can pass through them as more than one type of fluid channel can be printed on one metal sheet, almost any arrangement is possible, even the counter-current arrangement is possible.
How does the Printed Circuit Heat Exchanger Technology work?
The Printed Circuit Heat Exchanger has a very simple working. It has separate entrances and exits for the different fluids, so they don’t mix. The two different fluids can enter and leave through these entrances and exits. The two fluids will enter the heat exchanger through their separate entries into the heat exchanger. Then both the different fluids will enter their respective fluid channels (usually, the fluid channels for different fluids are in alternating plates, e.g., Hot, cold, hot, cold). After the two fluids enter their fluid channel, they pass through the heat exchanger, where their heat will exchange.
The thin metal sheets allow the two fluids to have maximum contact with each other. These sheets are extremely thin with microscopic fluid channels. This way, maximum heat is exchanged between the two fluids. The fluids pass through several vessels in several plates before exiting. Then the two fluids leave the heat exchanger separately through their separate exits. This is how the heat exchanger works. You can control the fluid capacity of the printed circuit heat exchanger by adding nozzles through which you can control how much fluid enters, increase or decrease it as you desire.
Advantages of Printed Circuit Heat Exchanger
Manufacturers diffusion bond the metal sheets to create a solid block of metal with no gaskets, interlayers, or brazing. This also increases the efficiency of the heat exchanger as the extremely thin metal sheets allow maximum contact between the two fluids for efficient heat exchange. Moreover, multiple streams can flow through a single printed circuit heat exchanger. As they are capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, they are resistant to freezing as well. The heat exchanger can withstand extremely high pressures along with extremely high temperatures.
The Printed circuit heat exchangers are highly vibration-resistant due to the tight solid core. They are catastrophic failure resistant as they don’t have any tubes that will rupture. Hence, no tube failure occurs in shell and tube heat exchangers. Because of their small and compact size, they require less space and lighter weight than other heat exchangers. The small size and weight of PCHEs help in operational project savings for transport, handling, installation, and reducing pipework and other requirements during the connecting process.
Additionally, you can quickly achieve the close approach temperatures in a counter-flow configuration. As the printed circuit heat exchangers are made from thin metal sheets, corrosion-resistant metal alloys can be used, which are compatible with the fluid flowing through it, allowing no corrosion to occur.
Application
Printed circuit heat exchangers have many applications as they are smaller, more compact, and highly efficient, with several advantages. Some of the Printed circuit heat exchanger’s applications include;
- LNG Liquefaction
- LNG Regasification
- High-temperature recuperators
- LNG stripper reboilers
- Sour gas compression cooling
- Light MR/End flash gas interchangers
- LNG carrier fuel gas heaters
- LNG superheaters
- Floating LNG exchangers
- LNG recovery
- LNG chillers and pre-coolers
- Fuel gas performance heaters
- Fuel gas preheaters and superheaters
- Gas compressor coolers
- Fuel cell chillers or pre-coolers
- Freeze resistant/protection applications
- Compressor discharge coolers
- Micro gas turbine recuperators
- Turbine regenerators
- Kettle reboilers
- Waste heat recovery unit (WHRU)
- Feedwater heaters
- Air pre-heaters
- Inlet coolers and chillers
- Compressor intercoolers and aftercoolers
- Hydrogen or CO2 chillers and pre-coolers
- Rotary air, lube oil, quench coolers
- After chillers and aftercoolers
- Regenerators
- Economizers
- Condensers
- Supercritical CO2 recuperators
- Botanical extraction applications
Printed circuit Heat Exchangers are a more advanced type of heat exchanger. They have many more advantages than other heat exchangers. The most significant characteristic of the PCHEs that makes them much better than others is the micro-sized fluid channels and the diffusion bonding of the thin metal sheets.
Both these characters give the PCHEs many benefits, including efficient heat exchange, excellent withstanding capabilities of extremely high pressure and temperatures, small and compact design, vibration proof, freezeproof, cost-efficient when installing, and corrosion resistance due to the alloy metalcore, made from metals with the higher melting point only. These advantages make the printed circuit heat exchangers very beneficial in many different applications in many various industries.
Take Away
The printed circuit heat exchanger technology has become very popular across industries due to its numeorus benefits. Since the products hold great importance, therefore, it is imperative to choose the right manufacturer and supplier. Stollpche is among the leading suppliers in the industry. They offer quality at a reasonable price.
For more information, Contact Us Today!