What Are the Bonding Parameters of Vacuum Diffusion Bonding? What Are Their Effects?
The main bonding parameters of vacuum diffusion bonding are: temperature, pressure, heat preservation diffusion time and protective atmosphere, diffusion bonding of materials with phase change and ceramics and other brittle materials during the cooling process, and the heating and cooling speed should be controlled.
(1) Temperature
Temperature is the most important bonding parameter of vacuum diffusion bonding. Within a certain temperature range, the diffusion process accelerates with the increase of temperature, and the joint strength can also increase accordingly.
However, the increase in temperature is limited by conditions such as the high-temperature strength of the tool and fixture, the phase transformation and recrystallization of the weldment, and when the temperature is higher than a certain value, the impact on the quality of the joint is not significant.
Therefore, the heating temperature for solid-phase diffusion bonding of most metal materials is set at 0.6-0.8 Tm (K), where Tm is the melting point of the base material.
(2) Pressure
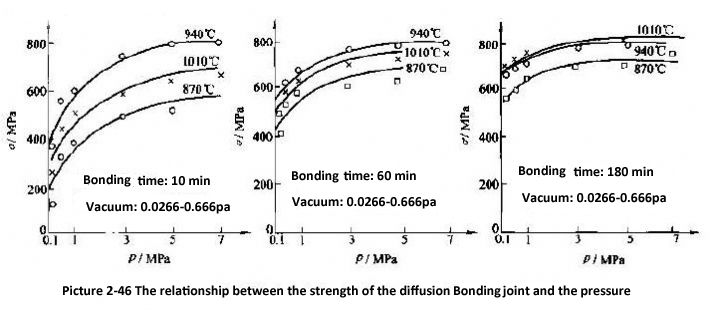
Pressure mainly affects the first and second stages of diffusion bonding. Higher pressure can obtain higher quality joints. The relationship between joint strength and pressure is shown in Figure 2-46.
When the weldment has a larger grain size or a larger surface roughness, the required pressure is also higher. The upper-pressure limit is limited by the overall deformation of the weldment and the equipment capacity. Except for hot isostatic pressure diffusion bonding, it is usually 0.5-50 MPa.
Considering the limitation of weldment deformation, the pressure can be selected within the range of Table 2-24. In view of the fact that the pressure has little effect on the first stage of diffusion bonding, it is allowed to reduce the pressure in the later stage of solid-phase diffusion bonding to reduce deformation.
| Material Type | Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel | Aluminum Alloy | Titanium Alloy |
| Ordinary Diffusion Pressure/Mpa | 5-10 | 7-12 | 3-7 | —— |
| Hot Isostatic Pressure Diffusion Pressure/Mpa | 100 | —— | 75 | 50 |
Common pressure for solid-phase diffusion bonding of the same metal
(3) Thermal diffusion time
The heat preservation diffusion time is not an independent variable, but is closely related to temperature and pressure, and can vary within a wide range.
When using higher temperature and pressure, it only takes a few minutes; otherwise, it takes several hours. Diffusion bonding with an intermediate layer also depends on the thickness of the intermediate layer and the requirements for the joint composition and uniformity of the structure.
It must be pointed out that short heat preservation and diffusion time will affect the quality of joints, and too long time will also cause adverse effects, which is manifested by the growth of the grains of the base material and the decrease in toughness. For joints that may form brittle intermetallic compounds, the diffusion time should be controlled to reduce the thickness of the brittle layer.
(4) Protective atmosphere
Diffusion bonding is divided into vacuum and non-vacuum. Non-vacuum diffusion bonding is usually carried out in a protective atmosphere, with Ar as the protective gas, and some materials can also use H2, He, or high-purity nitrogen.
The vacuum degree of vacuum diffusion bonding is (1~20)×10-3Pa, and the diffusion in a vacuum is shorter than that of normal pressure argon protection under the same other parameters.
For more questions, please contact us!