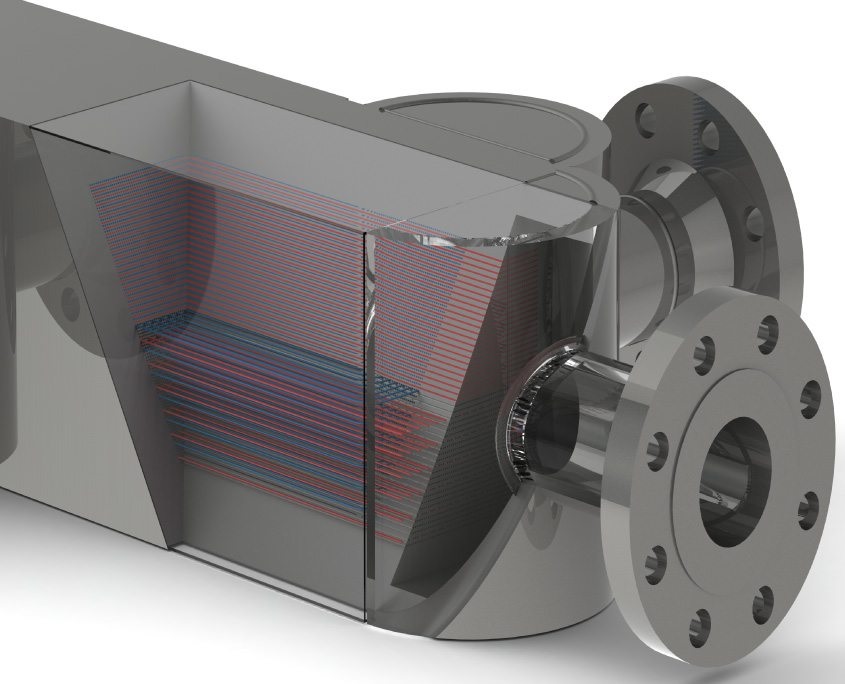
What are Diffusion Bonded Microchannel Heat Exchangers?
US Department of Energy states, “Diffusion bonding is a solid-state bonding process in which coalescence of faying surfaces takes place. The coalescence takes place by the application of pressure and elevated temperature. This process does not need any filler metal nor does it involve any macroscopic deformation. The joining materials retain their original strength.” A common application for diffusion bonding is compact heat exchangers. Diffusion bonded microchannel heat exchangers involve the bonding of flow plates in a heat exchanger ‘stack’. The process takes place under high pressure and controlled temperature and does not deform or melt the joining plates. The atoms of the etched plates merging into one another during diffusion bonding result in the strong all-metal heat exchanger. After bonding, it is possible to obtain precise internal flow passages within the block.
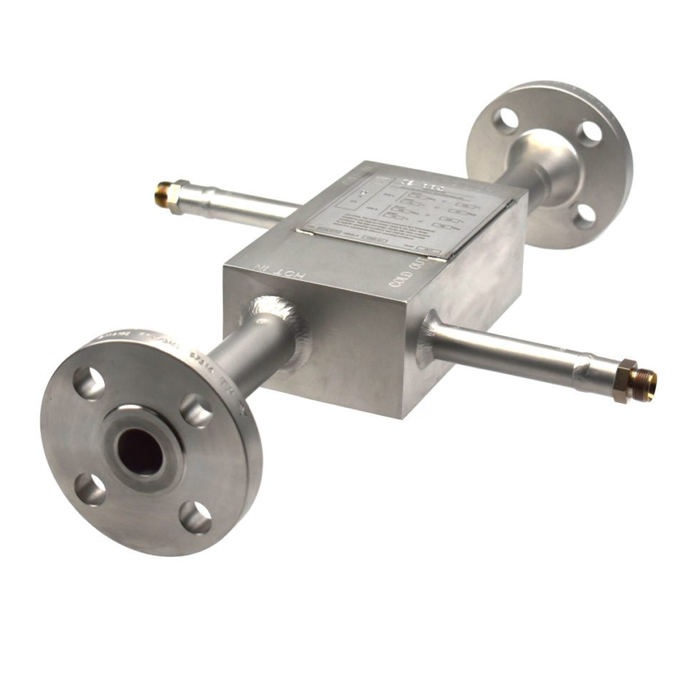

The Goal of Diffusion Bonded Microchannel Heat Exchangers
The demand for efficiency, compactness, and safety requires an exceptional heat transfer. The plate-type microchannel heat exchangers combine compactness, high efficiency, low-pressure drop, and the capacity to function with a high-pressure variance between cold and hot sides. Thus, the overall goal of microchannel heat exchangers is to improve the overall heat transfer. Resultantly, it reduces the temperature difference between a refrigerant and the air. Further, the microchannel heat exchanger reduces airside pressure drop leading to saving energy consumption.
The diffusion bonded microchannel heat exchangers are the perfect solution for critical applications requiring high efficiency and reliability under extreme pressure and temperature option. The heat exchangers have the advantage of resisting high temperatures and pressure. They are a high heat transfer coefficient due to their small volume and lightweight. The high-pressure resistance is up to 100 MPa. MCHE manufacturer Stoll uses stainless steel and other materials in microchannel heat exchangers to serve a wide range of applications.
Structure of Diffusion Bonded Microchannel Heat Exchangers
A diffusion bonded microchannel heat exchanger, also known as a printed circuit heat exchanger has the following fabrication.
- Design of heat exchanger
In the first step, the thermal engineering team works out the design required to make the microchannel heat exchanger.
- Plates etching
In the later stage, plates are etched with the flow design.
- Plate Assembling
Etching plates or shims assemble in a counter flow configuration.
- Diffusion bonding takes place
The fourth step involves diffusion bonding of stacked plates to construct a solid heat exchanger core. There are no gaskets in it. The diffusion bonding maintains the parent material strength throughout the core of the heat exchanger.
- Machining
After the diffusion bonded core, machining takes place. After this comes the joining the required manifolds, flanges, and components to the core of the heat exchanger.
- Cleaning and testing
This procedure ensures that the diffusion bonded microchannel heat exchangers are leakproof.
Diffusion Bonded Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers
The microchannel printed circuit head exchange is a relatively new concept. Its fabrication involves diffusion-bonding thin metal plates on the surface of which millimeter-scale semicircular fluid-flow channels are photochemically milled. This process corresponds to the one used for the construction of electronic printed circuit boards. After stacking, the diffusion bonded plates together fabricate a heat exchanger core.
PCHE design varies for different tasks. The complex shape of microchannel PCHEs on the stacking sheet surface requires an even load on the contact surface. This results in forming highly uniform quality bonds. A microchannel PCHE created through diffusion bonding carries superior bonding strength. It is also excellent heat resistance. The diffusion bonded microchannel PCHEs have a wider role to play in the chemical reaction process, refrigeration, and air conditioning systems. For example, there are diffusion bonded PCHEs for solar thermal power. The thermal design of PCHEs subjects to minimal constraints. Fluids may be liquid or gas and flow arrangements are countercurrent. A very close temperature approach in counter-flow leads to achieving high heat exchange effectiveness.
Due to their corrosion resistance quality, the diffusion bonded microchannel PCHEs are used for offshore oil and gas exploitation. Stoll is the first Asian company who has successfully developed the first domestic offshore oil and gas open using PCHE. The other competitors in the same field are Vacuum Process Engineering. With increasing pollution levels and rapidly reducing natural resources, the need for energy-saving and low emission heat exchangers has surged. Keeping this in view, Stoll’s PCHEs have penetrated the petrochemical industries. They are the first ones to create the first printed circuit heat exchanger for the petrochemical industry in China.
Applications of Diffusion Bonded PCHEs
The top industrial applications of microchannel printed circuit board heat exchangers are:
- Hydrocarbon gas and gas condensate processing
- Fine chemicals
- Chemical processing
- Electricity and energy
- Refrigeration
Benefits of Diffusion Bonded Microchannel Heat Exchangers
- The high-efficiency heat exchange design incorporates the features of microchannels and diffusion bonding manufacturing.
- The diffusion bonding of the heat exchanger core creates a solid core without brazing, interlays, or gaskets.
- The core design withstands extreme pressures of the two streams at the highest temperature. As a result, safety is improved.
- Microchannel heat exchangers are amazingly resilient to vibrations, catastrophes, and freezing.
- The highly compact construction of MCHEs results in savings through low eight and fluid inventory.
- The remarkable compact size and high corrosion resistance of MCHEs is due to the use of stainless steel and other materials makes. As a result, diffusion bonded MCHEs are the perfect choice for offshore facilities.
- The small hydraulic diameter of channels is highly demanded in HVAC due to their multiple technical benefits.
Summary
The efficient transfer of energy for industrial applications depends on the ability to incorporate effective heat exchangers. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting microchannel technology in heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration products. They do so because this technology has benefits like enhanced energy efficiency, reduced refrigerant cost. The need for efficient transfer of energy, compactness, and safety challenge has led the way to the creation of diffusion bonded microchannel heat exchangers. Modern diffusion bonded compact heat exchangers provide high compactness, low-pressure drop, and high effectiveness. In addition, they can operate under high-pressure variance between cold and hot sides.




